Voice conversion software - Voice conversion (VC) is a technique to convert a speaker identity of a source speaker into that of a target speaker. This software enables the users to develop a traditional VC system based on a Gaussian mixture model (GMM) and a vocoder-free VC system based on a differential GMM (DIFFGMM) using a parallel dataset. Direct-and-indirect-speech-worksheets-for-grade-5 - Your Home Teacher. Direct and Indirect Speech - English ESL Worksheets for distance learning and physical classrooms. Grade 6 Grammar Lesson 13 Direct and indirect speech Direct and indirect speech, Indirect speech, Grammar lessons.
- Advertisement
- SYNTPARSE German v.2.0Parses the German sentence showing its grammatical and syntactical constituent elements: subject, object (direct, indirect), complement (subject, object, infinitival complement), verb and verbal tense ( present tense, past tense, future tense), mood, ...
- SYNTPARSE English v.2.0Parses the English sentence showing its grammatical and syntactical constituent elements: subject, object (direct, indirect), complement (subject, object, infinitival complement), verb and verbal tense ( present tense, past tense, future tense), ...
- Domain Administration Tool v.3.20Manage security, servers, networks and workstations. Features include combined changes on users, information on indirect group memberships, import and export of domain information, multiple form user rights, customizable overview of server properties ...
- Venables v.1.5.1Abstract two-player strategy game with novel features, including a unique indirect method of controlling pieces. Easy to learn - practise against the computer at any of 10 difficulty levels.
- BackLinks Master v.1.3Use BackLinks Master to find all the backlinking sites in a fast, easy way. You can check a link's anchor text, its status, if it's direct or indirect, and export all info in a CSV report for further analysis.
- Beaded Jewelry Software v.v1.0Jewelry Pricing Software. Correctly calculate wholesale and retail prices of your jewelry instantly. Account for your hours that you work and includes your overhead costs as well as other indirect costs. From the creators of Bead Manager Pro - the ...
- The Complete Genealogy Reporter v.2013Create comprehensive narrative GEDCOM reports and books with fully cross-referenced texts, notes, media, and family tree diagrams. The Complete Genealogy Reporter can incorporate all cousins, aunts, uncles, and indirect relationships via marriage.
- WideStream v.1.0.5.864 Beta 1WideStream supports multi-threaded downloads, download by ranges (can interrupt and continue downloads at any moment), direct and indirect HTTP downloads, HTTP redirects, FTP downloads, network traffic management, download priorities, host manager ...
- Brutus v.2006Brutus is developed and tested with the utmost care. However, Brutus is freeware and provided as is, without warranties of any kind. The copyright holder is not responsible for any direct or indirect consequence of using this software. Brutus is ...
- BioXTAS RAW v.0.99.8.3bBioXTAS RAW is a program for analysis of Small Angle X-ray Scattering data. The software enables data reduction from the 2D detector image, data manipulation and masking and provides analysis of 1D data by the Bayesian Indirect Fourier ...
- FreePBX v.2.6.0beta1FreePBX is the most widely deployed Asterisk based PBX application with over 3 million direct and indirect downloads. It transforms your LAMPA stack into a powerful PBX. See http://www.freepbx.org for Forums, Docs, Bug Tracker, Project Site and ...
- Text based C++ Ask class library v.1.0Ask objects prompt a user for an object repeatedly until valid data is entered. Help messages are displayed based upon user inputs or errors. Supports various natural languages. Handles journaling and mixed indirect input from files and user keyboard ...
- Freeboard: OSS board game client/server v.1.0freeboard is aimed as being a free opensource server/client for setting up community boardgames servers.It supports:- one to one direct connection- one to one indirect connection (behind proxies)- one to server connectiongraphical client availabl ...
- QSimpleCompression v.1.0A Qt library for simple file-compression, it is especially designed for direct and indirects formal Bigraph model with the indirect communication abstraction of Gelernter's tuple-space, i.e. a coordination system based on bigraphs.
- Easyudc v.1.0Project for an easy creation of client/server aplications thant need a basic user autentification alrady supported, indirect database access with full support, message protocol and the posibiliti of implement new features in it.
- GDirectLinks for Safari v.1.0.3Blocks the substitution of direct links with indirect ones in Google Search results.
- DOTX to DOCX Converter v.10.1This application easily convert DOTX files to DOCX.
- Synthis Process Monitor v.4.0The fastest way to capture and share your business process knowledge.
- TomP2P v.4.0.5TomP2P is an extended DHT, which stores multiple values for a key.
- SYNTPARSE English Parses the English sentence showing its grammatical and
- Amazon AffiliateSide Script/Manager The Amazon AffiliateSide script has been improved to offer
- SYNTPARSE German Parses the German sentence showing its grammatical and
- APS Accounting & Stock Control Easy to utilize multy currency Accounting & Stock direct
- The Complete Genealogy Reporter Create comprehensive narrative GEDCOM reports and books with
- BitKinex FTP Client BitKinex integrates the functionality of an innovative FTP
- Visral Parser Gen, Syntax Diagram Editor VISRAL PG generates parsers and state machines directly
- Beaded Jewelry Software Jewelry Pricing Software. Correctly calculate wholesale and
- Cheetah3D Cheetah3D 5.6 brings you a flexible and professional 3D
- SYNTPARSE - English Grammatical analysis of the English sentence
 Visit HotFiles@Winsite for more of the top downloads here at WinSite!
Visit HotFiles@Winsite for more of the top downloads here at WinSite!Direct and Indirect Speech
Direct and indirect speech can be a source of confusion for English learners. Let’s first define the terms, then look at how to talk about what someone said, and how to convert speech from direct to indirect or vice-versa.
You can answer the question What did he say? in two ways:
• by repeating the words spoken (direct speech)
• by reporting the words spoken (indirect or reported speech).
Direct Speech
Direct speech repeats, or quotes, the exact words spoken. When we use direct speech in writing, we place the words spoken between quotation marks (” “) and there is no change in these words. We may be reporting something that’s being said NOW (for example a telephone conversation), or telling someone later about a previous conversation.
Examples
• She says, “What time will you be home?”
• She said, “What time will you be home?” and I said, “I don’t know! ”
• “There’s a fly in my soup!” screamed Simone.
• John said, “There’s an elephant outside the window.”
Indirect Speech
Reported or indirect speech is usually used to talk about the past, so we normally change the tense of the words spoken. We use reporting verbs like ‘say’, ‘tell’, ‘ask’, and we may use the word ‘that’ to introduce the reported words. Inverted commas are not used.
She said, “I saw him.” (direct speech) = She said that she had seen him. (indirect speech)
‘That’ may be omitted:
She told him that she was happy. = She told him she was happy.
‘Say’ and ‘tell’
Use ‘say’ when there is no indirect object:
He said that he was tired.
Always use ‘tell’ when you say who was being spoken to (i.e. with an indirect object):
He told me that he was tired.
‘Talk’ and ‘speak’
Use these verbs to describe the action of communicating:
He talked to us.
She was speaking on the telephone.
Use these verbs with ‘about’ to refer to what was said:
He talked (to us) about his parents.
What is reported speech?
Reported speech is when you tell somebody else what you or a person said before.
Distinction must be made between direct speech and reported speech.
Direct speech vs Reported speech:
Direct speech Reported speech
She says: “I like tuna fish.” She says that she likes tuna fish.
She said: “I’m visiting Paris next weekend” She said that she was visiting Paris the following weekend.
Different types of sentences
When you use reported speech, you either report:
• statements
• questions
• requests / commands
• other types
A. Reporting Statements
When transforming statements, check whether you have to change:
• pronouns
• tense
• place and time expression
1- Pronouns
In reported speech, you often have to change the pronoun depending on who says what.
Example:
She says, “My dad likes roast chicken.” – She says that her dad likes roast chicken.
2- Tenses
• If the sentence starts in the present, there is no backshift of tenses in reported speech.
• If the sentence starts in the past, there is often backshift of tenses in reported speech.

Direct speech Reported speech
(no backshift) “I write poems.” He says that he writes poems.
(backshift) “I write poems.” He said that he wrote poems.
No backshift
Do not change the tense if the introductory clause is in a present tense (e. g. He says). Note, however, that you might have to change the form of the present tense verb (3rd person singular).
Example:
He says, “I write poems.” – He says that he writes English.
Backshift
You must change the tense if the introductory clause is in a past tense (e. g. He said).
Example:
He said, “I am happy.” – He said that he was happy.
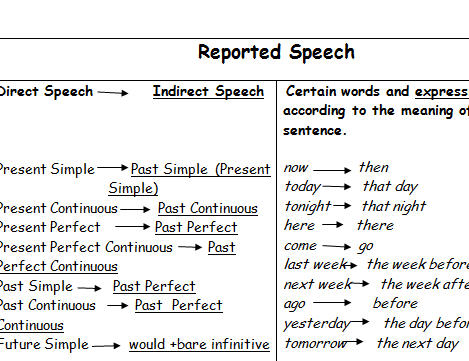
Examples of the main changes in tense:
Direct Speech Reported Speech
Simple Present
He said: “I am happy” Simple Past
He said that he was happy
Present Progressive
He said: “I’m looking for my keys” Past Progressive
He said that he was looking for his keys
Simple Past
He said: “I visited New York last year” Past Perfect Simple
He said that he had visited New York the previous year.
Present Perfect
He said: ” I’ve lived here for a long time ” Past Perfect
He said that he had lived there for a long time
Past Perfect
He said: “They had finished the work when I arrived” Past Perfect
He said that they had finished the work when he had arrived”
Past Progressive
He said: “I was playing football when the accident occurred” Past Perfect Progressive
He said that he had been playing football when the accident had occurred
Present Perfect Progressive
He said:”I have been playing football for two hours.” Past Perfect Progressive
He said that he had been playing football for two hours
Past Perfect Progressive
He said: “I had been reading a newspaper when the light went off” Past Perfect Progressive
He said that he had been reading a newspaper when the light had gone off
Future Simple (will+verb)
He said: “I will open the door.” Conditional (would+verb)
He said that he would open the door.
Conditional (would+verb)
He said: “I would buy Mercedes if I were rich” Conditional (would+verb)
He said that he would buy Mercedes if he had been rich”
The modal verbs could, should, would, might, needn’t, ought to, used to do not normally change.
Example:
He said, “She might be right.” – He said that she might be right.
Other modal verbs may change:
Modal Direct speec Repored speech
can “I can do it.” He said he could do it.
may “May I go out?” He wanted to know if he might go out.
must “She must apply for the job.” He said that she must/had to apply for the job.
will “They will call you.” He tod her that they would call her.
3- Place, demonstratives and time expressions
Place, demonstratives and time expressions change if the context of the reported statement (i.e. the location and/or the period of time) is different from that of the direct speech.
In the following table, you will find the different changes of place; demonstratives and time expressions.
Direct Speech Reported Speech
Time Expressions
today that day
now then
yesterday the day before
… days ago … days before
last week the week before
next year the following year
tomorrow the next day / the following day
Place
here there
Demonstratives
this that
these those
B. Reporting Questions
When transforming questions, check whether you have to change:
• pronouns
• place and time expressions
• tenses (backshift)
Also note that you have to:
• transform the question into an indirect question
• use the question word (where, when, what, how) or if / whether
Types of questions Direct speech Reported speech
With question word (what, why, where, how…) “Why” don’t you speak English?” He asked me why I didn’t speak English.
Without question word (yes or no questions) “Do you speak English?” He asked me whether / if I spoke English.


C. Reporting requests / commands
When transforming requests and commands, check whether you have to change:
• pronouns
• place and time expressions
Direct speech Reported speech
“Nancy,do the exercise.“ He told Nancy to do the exercise.
“Nancy, give me your pen, please.” He asked Nancy to give him her pen.
Tenses are not relevant for requests – simply use to / not to + verb (infinitive without “to”)
Example:
She said, “Sit down.” – She asked me to sit down.
She said, “don’t be lazy” – She asked me not to be lazy
For affirmative use to + infinitive (without to)
For negative requests, use not to + infinitive (without to).
Direct To Indirect Speech Converter software, free download
D. Other transformations
• Expressions of advice with must, should and ought are usually reported using advise / urge.
Example:
“You must read this book.“
He advised / urged me to read that book.
• The expression let’s is usually reported using suggest. In this case, there are two possibilities for reported speech: gerund or statement with should.
Example:
“Let’s go to the cinema.“=
1. He suggested going to the cinema.
2. He suggested that we should go to the cinema.
Main clauses connected with and/but
If two complete main clauses are connected with ‚and or ‚but, put ‚that after the conjunction.
Example:
He said,“I saw her but she didn’t see me.“ – He said that he had seen her but that she hadn’t seen him.“
If the subject is dropped in the second main clause (the conjunction is followed by a verb), do not use ‚that‘.
Example:
She said,“I am a nurse and work in a hospital.“ – He said that she was a nurse and worked in a hospital.“
http://www.myenglishpages.com/site_php_files/grammar-lesson-reported-speech.php
Grammar Exercise – Reported Speech
________________________________________
Do the exercise below on reported speech and click on the button to check your answers.
(Before doing the exercises you may want to read the lesson on reported speech)
Complete the sentences in reported speech.
1. John said, “I love this town.”
John said
2. “Do you like soccer ?” He asked me.
He asked me
3. “I can’t drive a lorry,” he said.
He said
4. “Be nice to your brother,” he said.
He asked me
5. “Don’t be nasty,” he said.
He urged me
6. “Don’t waste your money” she said.
She told the boys
7. “What have you decided to do?” she asked him.
She asked him
8. “I always wake up early,” he said.
He said
9. “You should revise your lessons,” he said.
He advised the students
10. “Where have you been?” he asked me.
He wanted to know
Warning
Before submitting the test, check the following:
• Punctuation and capitalization
• Spelling
• Spaces (don’t add any unnecessary spaces)
Direct Speech Converter
Answer
Do the exercise below on reported speech and click on the button to check your answers.
(Before doing the exercises you may want to read the lesson on reported speech)
Complete the sentences in reported speech.
1. John said, “I love this town.”
John said that he loved that town.
2. “Are you sure?” He asked me.
He asked me if / whether I liked soccer.
3. “I can’t drive a lorry,” he said.
He said that he couldn’t drive a lorry.
4. “Be nice to your brother,” he said.
He asked me to be nice to my brother.
5. “Don’t be nasty,” he said.
He urged me not to be nasty.
6. “Don’t waste your money” she said.
She told the boys not to waste their money.
7. “What have you decided to do?” she asked him.
She asked him what he had decided to do.
8. “I always wake up early,” he said.
He said that he always woke up early.
9. “You should revise your lessons,” he said.
He advised the students to revise their lessons.
10. “Where have you been?” he asked me.
He wanted to know where I had been.